Lower Back Pain in the Morning That Goes Away

Medically reviewed by Dr. Brian Paris, D.C on Nov. 6, 2018.
Here at The Healthy Back Institute, one of the most frequent questions we get from our readers is: What causes lower left side back pain?
But over the years, I've learned that what most people REALLY want to know is: What's the best way to get rid of lower left back pain?
Not surprisingly, the two go hand in hand. The answer is that pinpointing the cause is the key to quick and lasting pain relief.
That's not always an easy thing to do. This article covers some of the possible causes — as well as how to treat and prevent lower left side back pain.
The different types of pain
First, let's look at the different types of pain you might be experiencing. Being able to identify your pain can help you narrow down the cause.
By the way, these apply no matter where you're experiencing low back pain — whether it's on the lower left side or lower right side. They're even true if the pain you're experiencing is in your upper back, too.
Acute pain:
Some people experience lower left back pain as a sharp, stabbing pain. This is called acute pain.
Acute pain generally doesn't last a long time. When you injure yourself, like if you stepped on a nail, that's acute pain. It's immediate and often severe pain at the site of the injury. There's identifiable damage to tissue.
Eventually, acute pain goes away. Injuries heal, and the pain is gone.
Chronic pain:
When your pain persists even after the injury heals, we call that chronic pain. People usually describe chronic pain as "dull" or "aching."
If you injure your back, there are a lot of factors that can come into play which can lead to chronic pain. Your body's pain signal keeps telling your nervous system that it hurts, and the pain continues.
Chronic back pain is no joke. It can limit your daily activities and have a severe impact on your quality of life.
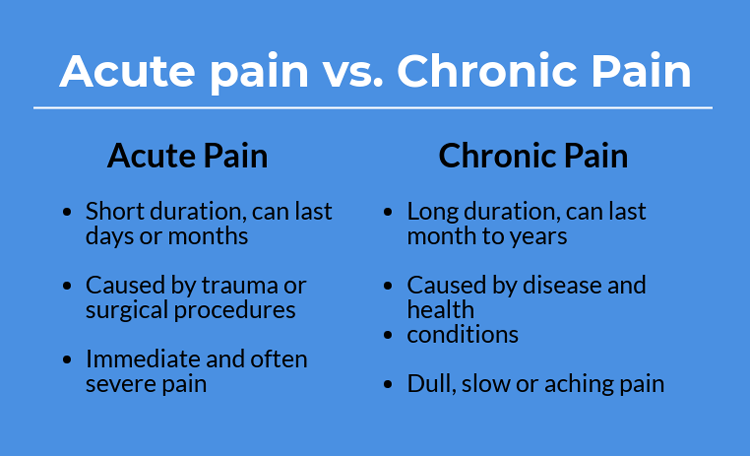
Breaking it down further, there are two general types of low back pain.
- Neuropathic pain: It's caused by nerve-tissue damage. One example of neuropathic pain would be a pinched nerve.
- Nociceptive pain: This type of pain occurs outside the nervous system. It includes things like arthritis.
Pain can occur anywhere in your back, but this article will focus solely on the most common causes and best treatment options for lower back pain that occurs on the left side.
Common causes of lower left back pain
There's no single cause for pain in the lower left side of your back. And it can take some time to figure out the root cause of your problem.
But here are a few of the most common causes:
- Muscle imbalances
- Bulging or herniated discs
- Muscle spasms, pulled back muscle
- Muscle strain, injury or trauma to the back muscles, ligaments or joints
- Trigger points
- Stress / Negative emotions
- Inflammation caused by diet
- Compression of one of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerve or the sciatic nerve
(Note: If lower left back pain is particularly severe, it may be an indication of a herniated or ruptured disc, or sciatica.)
This is far from a definitive list… and I'll tell you about a few more you should know about in just a minute. But first I want to talk a little more about muscle imbalances.
In more than a decade of researching the true causes of lower back pain (and all other types of back pain), I find muscle imbalances to be the least understood (and the most common).
What are muscle imbalances?
In simple terms, a muscle imbalance occurs when you have overdeveloped and tight muscles in one area of your body while the opposing muscles are weak and stretched out of their normal position.
These imbalances can happen anywhere in your body. They often develop as the result of the routine things you do while on the job, playing sports, or engaging in other activities you enjoy.
Over time, muscle imbalances can lead to other, more painful conditions. Things like:
- IT band syndrome
- SI joint syndrome
- Sciatica
- frozen shoulder
- knee pain, hip pain, and all forms of back pain (and yes, lower left side back pain)
Even if you've been to a doctor for your back pain (or sought any type of medical care, including chiropractic care), chances are they didn't even mention muscle imbalances. So don't feel bad if you're not familiar with the term.
The good news is there are effective treatments for muscle imbalances.
This video explains how muscle imbalances affect your pain and how you can correct them.
Loading the player...
(You can get a more detailed explanation of what muscle imbalances are, how they cause pain, and how to treat them by reading this post on Muscle Balance Therapy™.)
Other causes of lower left back pain
Does the pain in your lower left side extend through your buttocks?
This might be a sign that you have a tightened sacroiliac joint. That's the joint that connects the base of your spine to your pelvis.
The protection around the sacroiliac joint is less effective than other back joints.
That's because your sacroiliac doesn't have a disc. When a tightening of the sacroiliac joint occurs, you might feel pain in your buttocks, too.
Because as your sacroiliac joint tightens, so do the surrounding muscles and ligaments.
If it is your sacroiliac joint, many people find relief with chiropractic adjustments.
If you're experiencing lower left back pain or left side back pain, you'll want to keep a few other conditions in mind. Things like:
Urinary tract infection:
Along with pain, you may have a need to urinate frequently.
You may also have a burning sensation when urinating.
If your symptoms are accompanied by fever, chills, vomiting, nausea or abdominal pain, you may have a more serious infection… like a kidney infection.
These are serious warning signs that shouldn't be ignored. In that case, it's best to seek medical attention.
Irritable bowel syndrome:
Besides lower back pain, people with irritable bowel syndrome may also have abdominal pain, bloating, excessive gas, constipation, nausea, diarrhea, and cramping.
Although they shouldn't be confused with irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's and ulcerative colitis can also cause pain in the back and abdomen.
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a condition in which your body loses too much bone, doesn't make enough bone, or both.
Pain caused by osteoporosis is usually the result of a spinal compression fracture.
These types of fractures cause sudden, severe pain that are worse when you're standing or walking.
Spondylolysis:
This condition occurs when there is a defect or stress fracture in one of your vertebrae and is usually found in the lumbar vertebrae, or lower back.
Gallstones:
Your gallbladder is a small organ located just under your liver on the upper right side of your abdominal area. Inside your gall bladder is bile, a liquid substance that helps you digest your food.
Most gallstones are the result of having too much cholesterol in your bile. in fact, according to the folks at Harvard Health Publishing, up to 80 percent of gallstones fall into this category.[i]
Gallstones, which are more common in women, typically cause pain after you eat fatty foods. In some cases, the pain can radiate to other parts of your body, such as your chest or back.
Kidney stones or a kidney infection:
Kidney stones are made from minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys and often form when your urine is too concentrated.
They can affect any part of your urinary tract from your kidneys to your bladder and can be extremely painful to pass. Most back pain caused by kidney stones occurs when the stone or stones move within your kidney or passes into your ureter (the tube that connects your kidney and your bladder.)
Kidney infections most often occur when bacteria enter your urinary tract. According to the Mayo Clinic, symptoms of a kidney infection can include:[ii]
- Fever
- Chills
- Back pain, side pain(flank) or groin pain
- Abdominal pain
- Frequent urination
- Strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation or pain when urinating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pus or blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Urine that smells bad or is cloudy
Cauda equina syndrome
Although cauda equina syndrome (CES) is not common, this condition is a true medical emergency that requires a physician's intervention right away.
Cauda equina syndrome occurs when the bundle of nerves at the bottom of your spinal cord become compressed. Causes are varied, and can rage from a severed ruptured disc to a complication of an injury.
According to WebMD, symptoms of cauda equina syndrome include:[iii]
- Severe lower back pain
- Pain, numbness, or weakness in one or both legs that causes you to stumble or have trouble getting up from a chair
- Loss of or altered sensations in your legs, buttocks, inner thighs, backs of your legs, or feet that is severe or gets worse and worse. You may experience this as trouble feeling anything in the areas of your body that would sit in a saddle (called saddle anesthesia)
- Recent problem with bladder or bowel function, such as trouble eliminating urine or waste (retention) or trouble holding it (incontinence)
- Sexual dysfunction that has come on suddenly
General health and lifestyle issues
If you're a woman, lower left back pain may be a symptom of a gynecological disorder.
And, if you're overweight (especially if you're obese), this could be the culprit behind any pain you have in the left side of your lower back.
Generally speaking, weight loss and a healthy diet and lifestyle can significantly reduce lower back pain.
So what should you do to treat lower left back pain?
In my experience, most people can find relief for their lower back pain on their own with the right treatments and prevention techniques. (Of course, if you suspect you may have a serious underlying medical condition, you should seek medical attention.)
If you do seek mainstream medical advice for your lower back pain, you'll most likely have to undergo a physical exam as well as other tests, such as x-rays, ct scans or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
In most cases, doctors will prescribe a pill for pain relief or suggest you take over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs. These drugs can have serious side effects.
For the vast majority of people with left lower back pain, there are safe and natural treatment options available.
The following list of treatments has helped thousands of people around the world escape lower left back pain… and these methods could help you, too.
8 Best Treatments for left side back pain and lower left back pain
1. Muscle Balance Therapy™
I talked a bit about muscle imbalances above. The best way to treat them is with Muscle Balance Therapy™.
This approach uses the results of special, personalized muscle balance assessments to design an individually targeted program of corrective exercises.
These exercises will help take the stress off your muscles, joints and ligaments so you can achieve a more balanced body and eliminate the cause of your pain.
2. Massage therapy

Massage therapy can go a long way when it comes to easing lower back pain. In one 2011 study, 400 people with low back pain ranging from moderate to severe were divided into three groups.
The first group got a relaxing Swedish massage once a week. The second got a weekly massage that focused on muscles around the hips and lower back. The third group kept receiving their "usual care" — which could be anything from taking painkillers to seeing a chiropractor.
At the end of the 10-week study, both groups that got massages were doing better than the group that didn't get massages.[iv]
Many chiropractic offices have massage therapists on staff that can work with your chiropractor to deliver the most effective therapeutic plan for your particular type of pain.
3. Trigger point therapy 
Trigger points are the tight, aching knots you feel in your back (although can occur in other places like your hips and legs, too).
They can cause "referred pain," which means they can cause pain in seemingly unrelated parts of your body. Things like headaches and joint pain.
Trigger point therapy involves applying deep manual pressure to trigger points.
You can get this type of treatment from a skilled physical therapist, massage therapist, chiropractor or trigger point specialist.
4. Inversion/decompression therapy
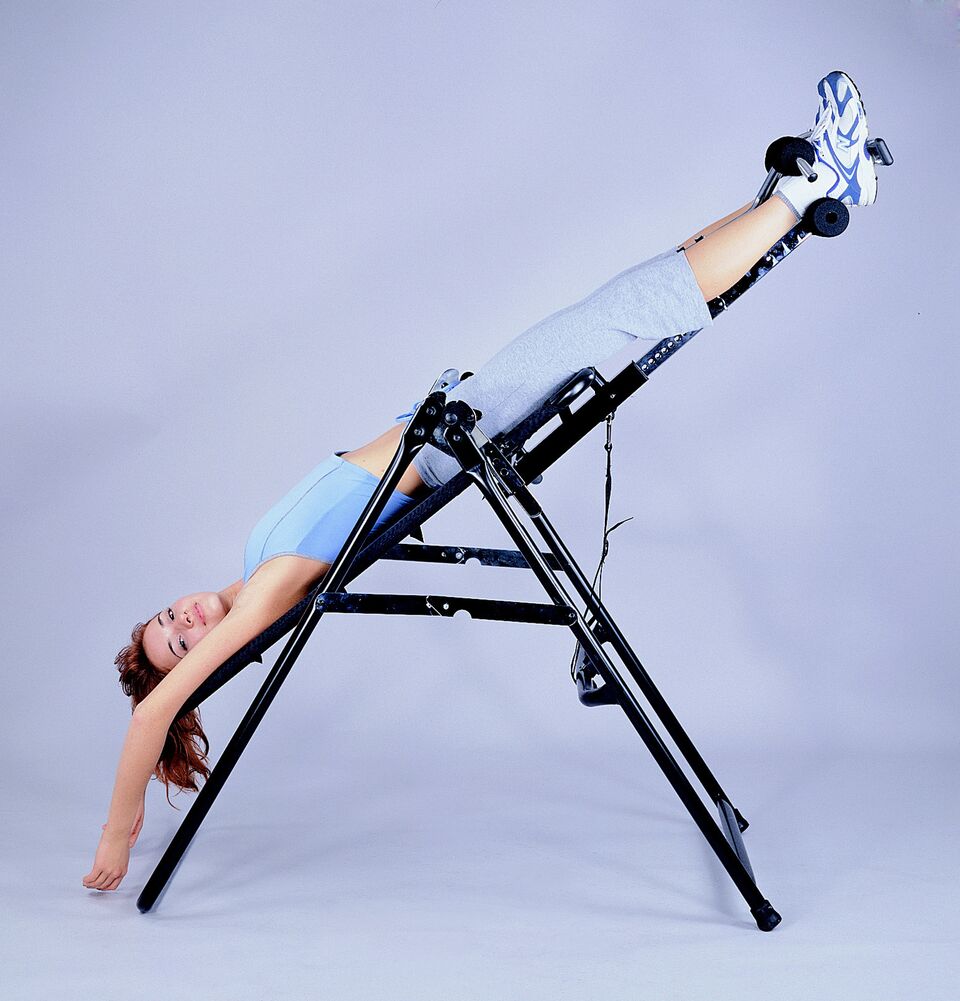

Just as the name implies, inversion therapy is when you hang from your feet upside-down to relieve pressure on your back and the discs in your vertebrae.
In a nutshell, inversion tables allow gravity and your own body weight to do all the work.
The therapy has been around for thousands of years, but modern medicine hasn't quite caught up yet.
Fortunately, that's starting to change. In 2012, researchers looked at two groups of patients who had sciatic pain and were scheduled for lumbar disc surgery.
One group received routine physiotherapy. The other group received physiotherapy AND inversion therapy.
Researchers found that the group that received inversion therapy were more than 70% less likely to need surgery than those who didn't try inversion therapy.[v]
Learn more about the many health benefits of inversion therapy and why it works right here.
5. Acupuncture/Acupressure
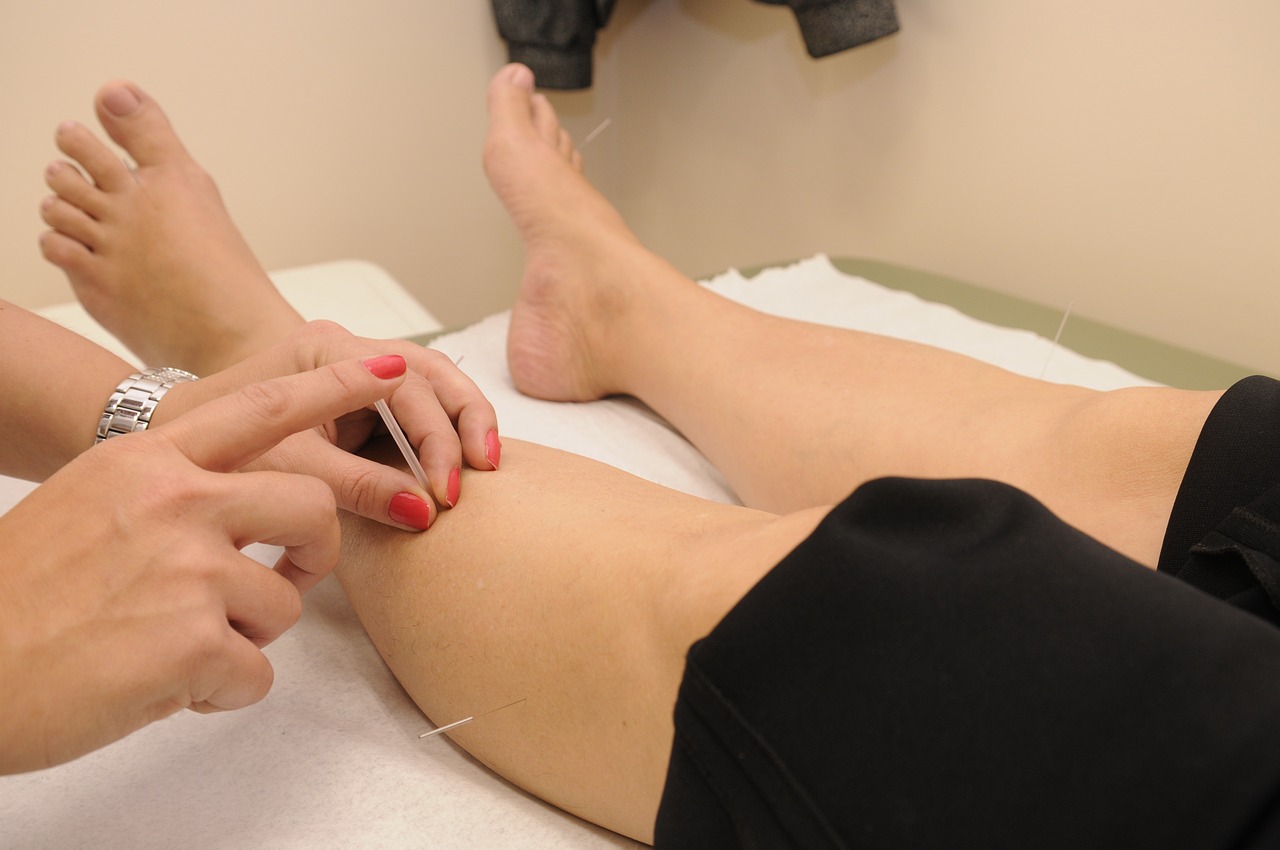
The ancient practice of acupuncture involves the insertion of very fine needles into targeted areas of pain and discomfort.
The Chinese believe this stimulates your inner energy, known as Chi. It's believed this process stimulates the production of endorphins and promotes blood flow to help speed up healing.
And studies show this healing art provides short-term relief for lower back pain. In fact, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) even supports its use.[vi]
Acupressure is another option. No needles are involved. Instead, the therapist applies pressure to targeted pain areas.
6. Relaxation, meditation, journaling
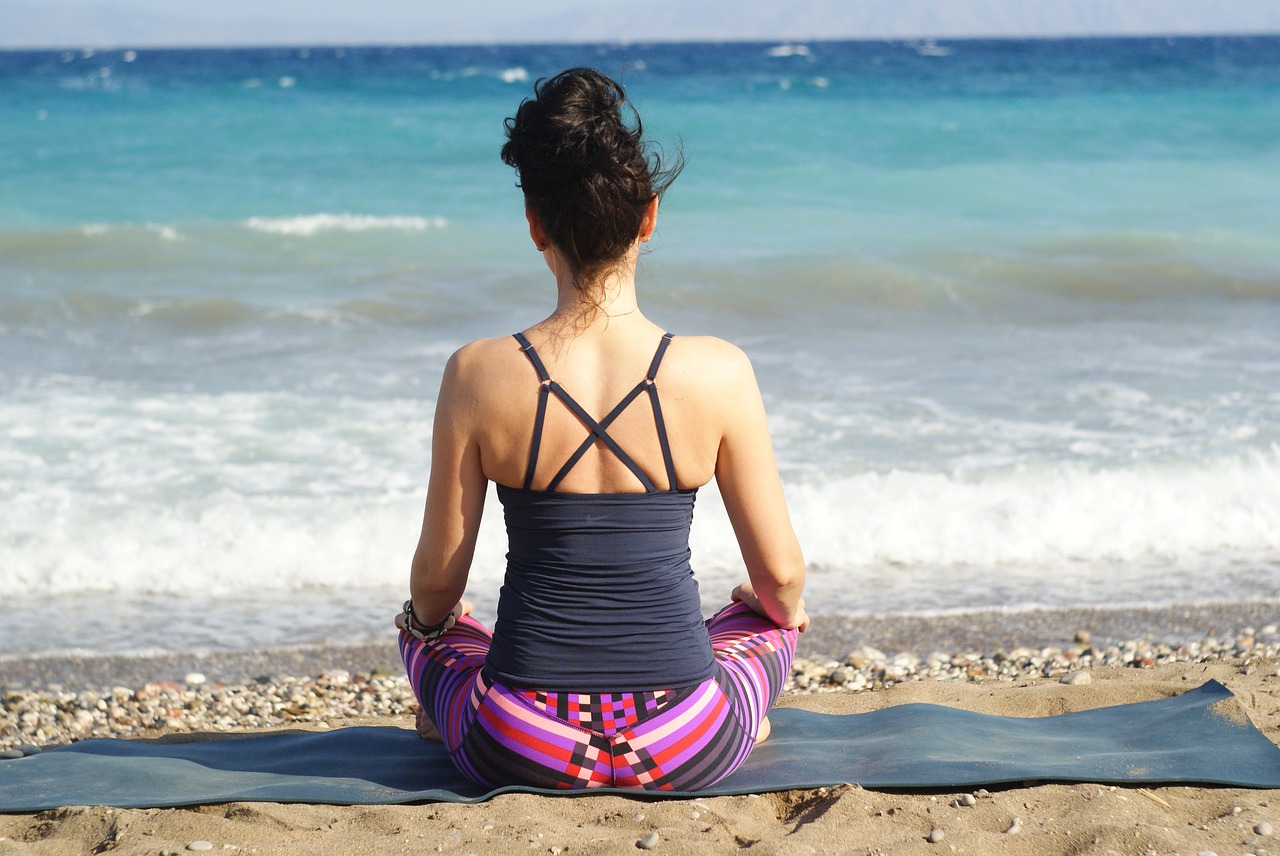

Stress is one of the biggest, and most underrated, underlying causes of back pain.
Negative thoughts, or even thinking about a stressful event, can trigger a chain of physical reactions in your body. Your muscles tighten — and this can cause imbalances that lead to pain.
That's why I always tell people how important to reduce stress as much as possible.
And practicing relaxation and meditation techniques, as well as journaling, have all been proven to have a positive effect on emotional well-being.
As little as 10 minutes being still, breathing deep, and centering your thoughts has been shown to quiet both mind and body after a stressful day.
7. Clean up your diet
Inflammation caused by many of the foods we eat today leads puts tremendous strain on your organs, muscles and nerve endings.
It triggers a breakdown in your back muscles and overwhelms your pain receptors. Some o the worst inflammation-causing foods are refined grains, dairy, omega-6 fatty acids, sugar and processed foods.
8. Drink more clean, filtered water
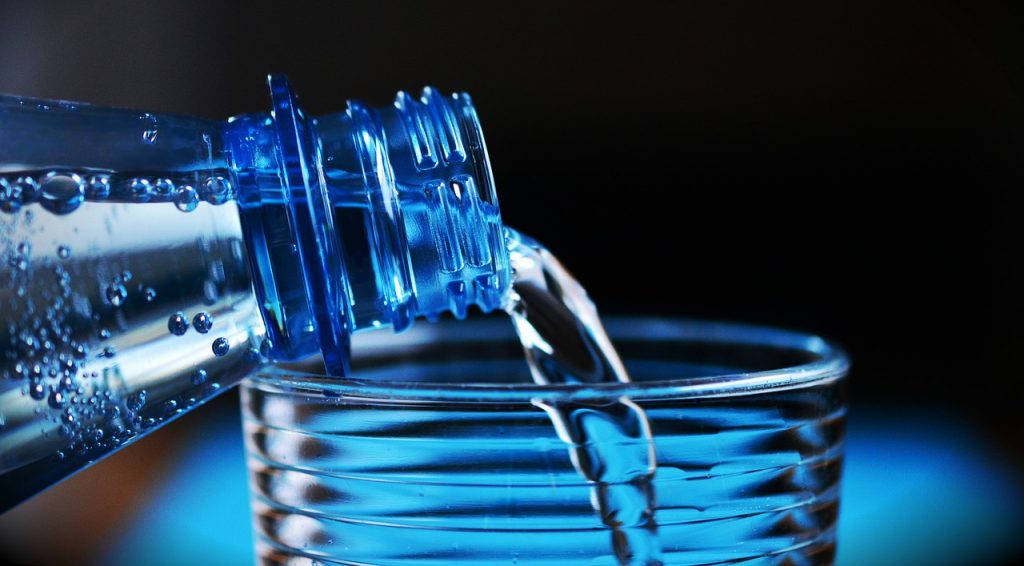

Water re-inflates the discs in your spine after they've been depleted throughout the day (Your discs are mostly made of water). It helps flush toxins out of your system. It cushions your muscles and helps your joints function more smoothly.
Eight glasses a day is a good general guideline for most people.
Left side back pain/lower left back pain prevention
I'm sure you've heard this saying before: "An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure." I'm a firm believer in that.
Here are a few things to keep in mind as you go about your day. Following these tips can help stop lower left side back pain before it starts.
Improve your posture:Your posture matters — a lot! Try to keep an upright position when walking and sitting. No slouching!
Lift the right way: Always, always, always use your legs when lifting heavy objects. Sure, you've heard that advice before, but it's too important not to repeat. Make sure you don't bend from the waist. You'll dramatically increase your risk of injury.
Build core strength: Exercises that strengthen your core (abdomen and back) will help reduce your chances of injury. I'm a big fan of pilates for building up core strength. As you strengthen your core muscles, you gain extra support for your spine, which not only helps relieve pain in the lower left side of your back (and the rest of your back, too), but also improves posture.
Stretch daily: Stretching improves circulation, reduces stress, makes you more flexible, and improves balance and coordination. The key is to focus on one major muscle group at a time, making sure to stretch muscles on both sides of your body. Start with just 5 minutes a day, and increase the amount of time you spend stretching by 5 minutes each week until you reach an hour.
Editor's note: This article has been reviewed by a member of our medical advisory board. The content provided is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Please consult with your physician if you have any questions about your health.
Read more:
This breakthrough program has helped thousands eliminate back pain
Lower pain right side causes, symptoms and treatments
What is sacroiliac joint dysfunction
References
i "What to do about gallstones." Harvard Health Publishing (www/health.harvard.edu) March 2011
ii "Kidney Infection." Mayo Clinic (mayoclinic.org) Accessed October 28, 2018.
iii "Cauda equina syndrome overview." WebMD (webmd.com) Accessed Oct. 28, 2018.
iv Cherkin DC, Sherman KJ, Kahn J, et al. A comparison of the effects of 2 types of massage and usual care on chronic low-back pain: a randomized, controlled trial.Annals of Internal Medicine.2011;155(1):1–9.
v Prasad, KS et al. "Inversion therapy in patients with pure single level lumbar discogenic disease: a pilot randomized trial." 2012;34(17):1473-80.
vi "Acupuncture-Like Treatments Improve Low Back Pain." National Institutes of Health (nih.gov) May 18, 2009.
Filed Under: Back Pain
Written By:
Lower Back Pain in the Morning That Goes Away
Source: https://losethebackpain.com/lower-left-back-pain-left-side-pain/
0 Response to "Lower Back Pain in the Morning That Goes Away"
إرسال تعليق